???
| Contents [0/72] |
| Object-Oriented Design & Patterns [1/72] |

| Chapter Topics [2/72] |
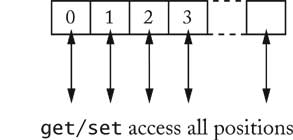
| List Iterators [3/72] |
LinkedList<String> list = . . .;
ListIterator<String> iterator = list.listIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
String current = iterator.next();
. . .
}
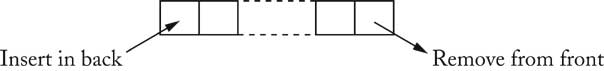
| Classical List Data Structure [4/72] |
Link currentLink = list.head;
while (currentLink != null)
{
Object current = currentLink.data;
currentLink = currentLink.next;
}
| High-Level View of Data Structures [5/72] |


| List with Cursor [6/72] |
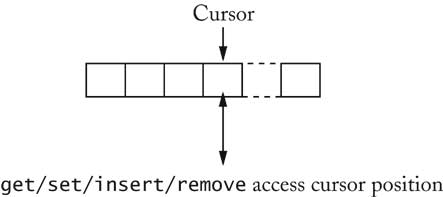
for (list.reset(); list.hasNext(); list.next())
{
Object x = list.get();
. . .
}
| The Pattern Concept [7/72] |
| Short Passages Pattern [8/72] |

| Short Passages Pattern [9/72] |
a lengthy description of the problem, including
| Short Passages Pattern [10/72] |
| Iterator Pattern [11/72] |
| Iterator Pattern [12/72] |
| Iterator Pattern [13/72] |
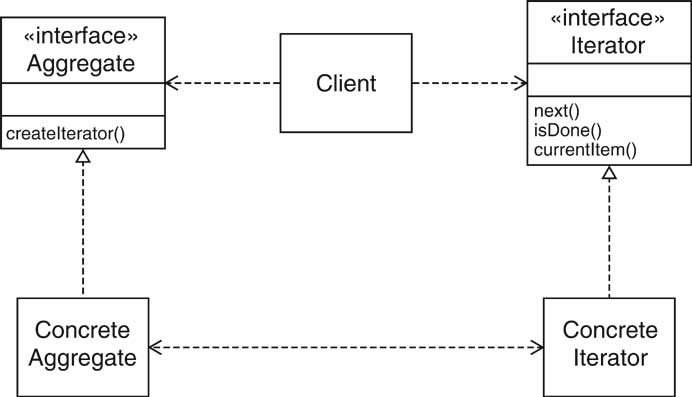
| Iterator Pattern [14/72] |
| Name in
Design Pattern |
Actual Name
(linked lists) |
| Aggregate |
List |
| ConcreteAggregate |
LinkedList |
| Iterator |
ListIterator |
| ConcreteIterator |
anonymous class implementing ListIterator |
| createIterator() |
listIterator() |
| next() |
next() |
| isDone() |
opposite of hasNext() |
| currentItem() |
return value of hasNext() |
| Model/View/Controller [15/72] |
| Model/View/Controller [16/72] |

| Model/View/Controller [17/72] |
| Model/View/Controller [18/72] |
| Model/View/Controller [19/72] |
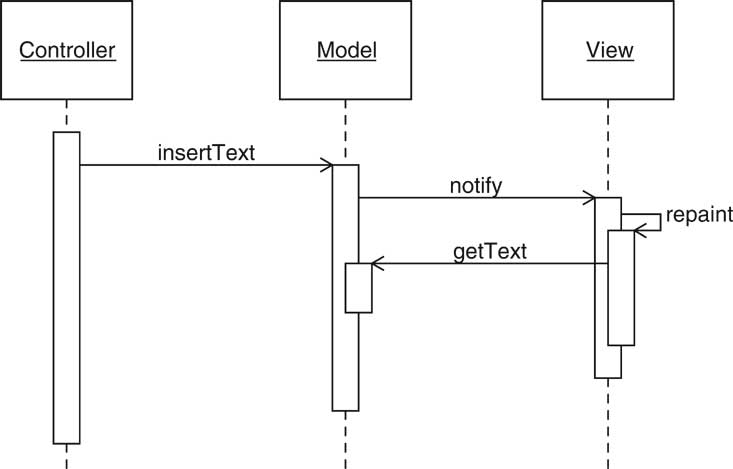
| Observer Pattern [20/72] |
| Observer Pattern [21/72] |
| Observer Pattern [22/72] |
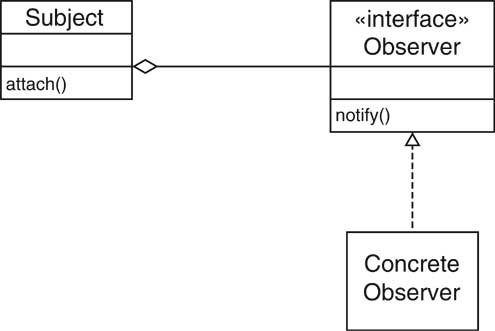
| Names in Observer Pattern [23/72] |
| Name in Design Pattern |
Actual Name (Swing buttons) |
| Subject |
JButton |
| Observer |
ActionListener |
| ConcreteObserver |
the class that implements the ActionListener
interface type |
| attach() |
addActionListener() |
| notify() | actionPerformed() |
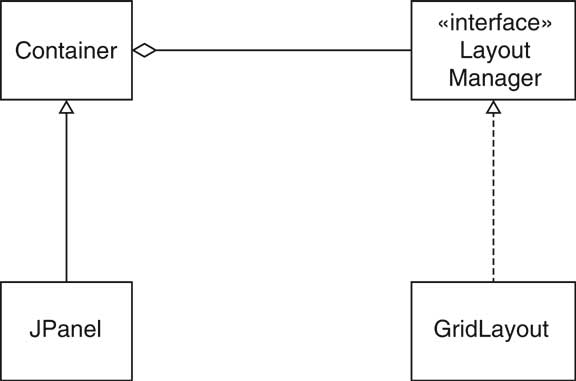
| Layout Managers [24/72] |
| Layout Managers [25/72] |
| Layout Managers [26/72] |
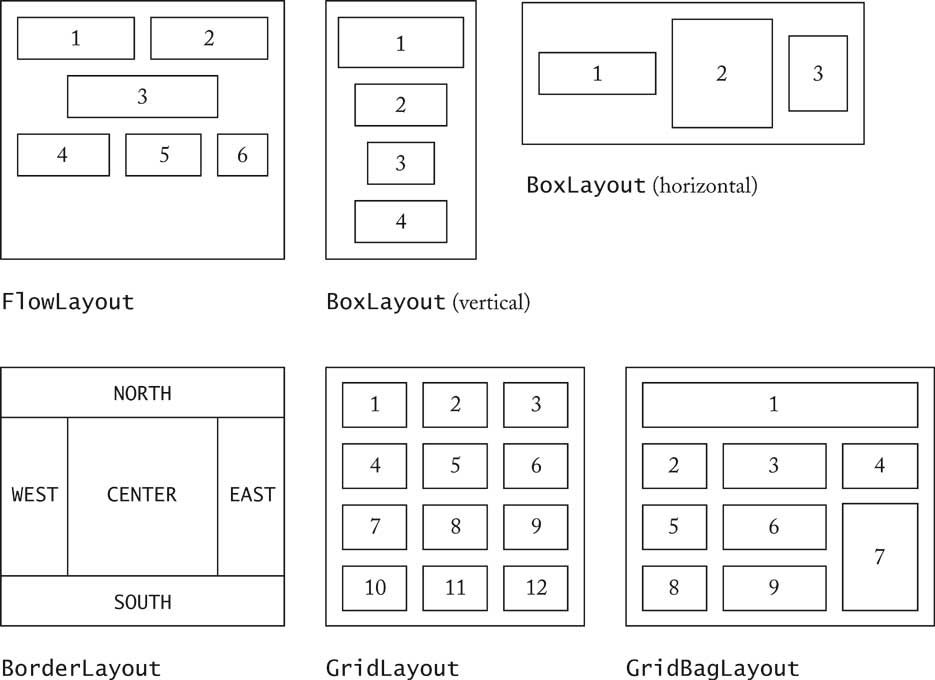
| Layout Managers [27/72] |
| Layout Managers [28/72] |
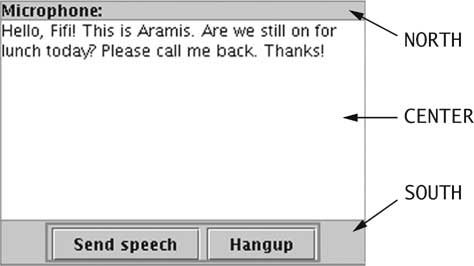
| Voice Mail System GUI [29/72] |
| Voice Mail System GUI [30/72] |


| Voice Mail System GUI [31/72] |
JPanel keyPanel = new JPanel();
keyPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 3));
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
JButton keyButton = new JButton(...);
keyPanel.add(keyButton);
keyButton.addActionListener(...);
}
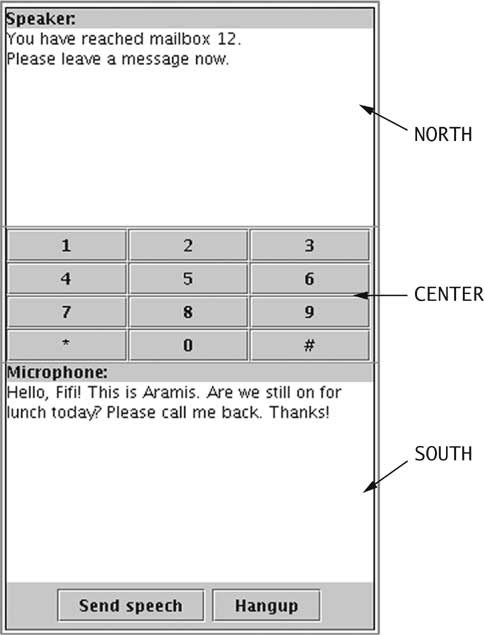
| Voice Mail System GUI [32/72] |
JPanel speakerPanel = new JPanel();
speakerPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
speakerPanel.add(new JLabel("Speaker:"), BorderLayout.NORTH);
speakerField = new JTextArea(10, 25);
speakerPanel.add(speakerField, BorderLayout.CENTER);
| Voice Mail System GUI [33/72] |
file:horstmann/ch05_mailgui/Telephone.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| Custom Layout Manager [34/72] |

| The LayoutManager Interface Type [35/72] |
public interface LayoutManager
{
void layoutContainer(Container parent);
Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent);
Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent);
void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp);
void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp);
}
| Form Layout [36/72] |
file:horstmann/ch05_layout/FormLayout.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
file:horstmann/ch05_layout/FormLayoutTester.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| Strategy Pattern [37/72] |
Comparator<Country> comp = new CountryComparatorByName();
Collections.sort(countries, comp);
| Strategy Pattern [38/72] |
| Strategy Pattern [39/72] |
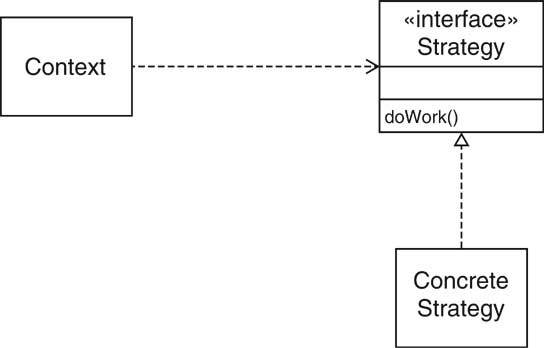
| Strategy Pattern: Layout Management [40/72] |
| Name in
Design Pattern |
Actual Name
(layout management) |
| Context |
Container |
| Strategy |
LayoutManager |
| ConcreteStrategy |
a layout manager such as BorderLayout |
| doWork() |
a method such as layoutContainer |
| Strategy Pattern: Sorting [41/72] |
| Name in
Design Pattern |
Actual Name
(sorting) |
| Context |
Collections |
| Strategy |
Comparator |
| ConcreteStrategy |
a class that implements Comparator |
| doWork() |
compare |
| Containers and Components [42/72] |
| Composite Pattern [43/72] |
| Composite Pattern [44/72] |
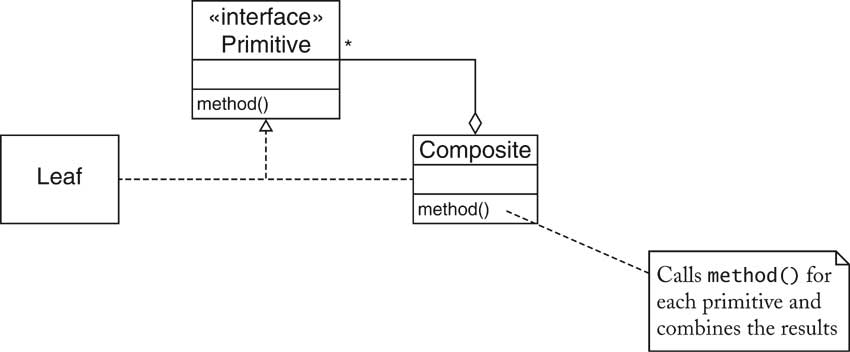
| Composite Pattern [45/72] |
| Name in
Design Pattern |
Actual Name
(AWT components) |
| Primitive |
Component |
| Composite |
Container |
| Leaf |
a component without children
(e.g. JButton) |
| method() |
a method of Component
(e.g. getPreferredSize) |
| Scroll Bars [46/72] |
JScrollPane pane = new JScrollPane(component);
| Scroll Bars [47/72] |
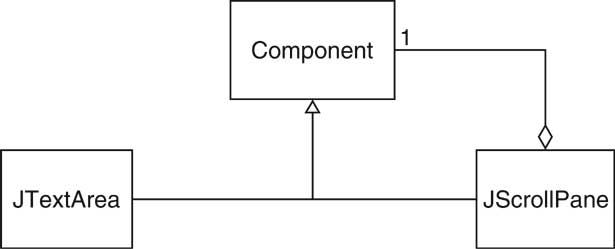
| Decorator Pattern [48/72] |
| Decorator Pattern [49/72] |
| Decorator Pattern [50/72] |
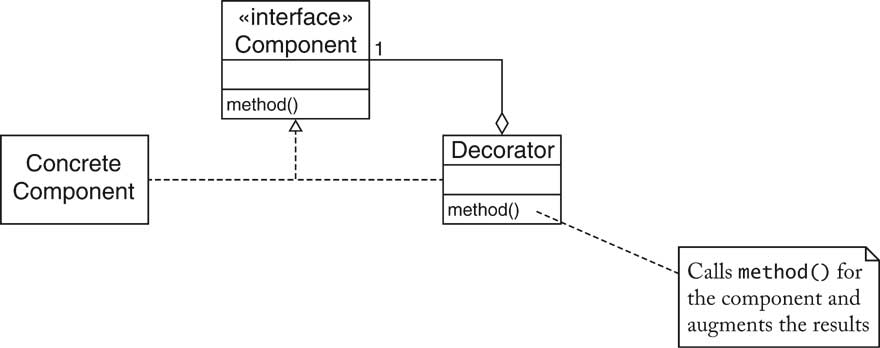
| Decorator Pattern: Scroll Bars [51/72] |
| Name in
Design Pattern |
Actual Name
(scroll bars) |
| Component | Component |
| ConcreteComponent | JTextArea |
| Decorator | JScrollPane |
| method() |
a method of Component
(e.g. paint) |
| Streams [52/72] |
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader console = new BufferedReader(reader);
| Decorator Pattern: Input Streams [53/72] |
| Name in
Design Pattern |
Actual Name
(input streams) |
| Component | Reader |
| ConcreteComponent | InputStreamReader |
| Decorator | BufferedReader |
| method() |
read |
| How to Recognize Patterns [54/72] |
| Litmus Test [55/72] |
Border b = new EtchedBorder()
component.setBorder(b);

| Litmus Test [56/72] |
| Putting Patterns to Work [57/72] |
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/LineItem.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/Product.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
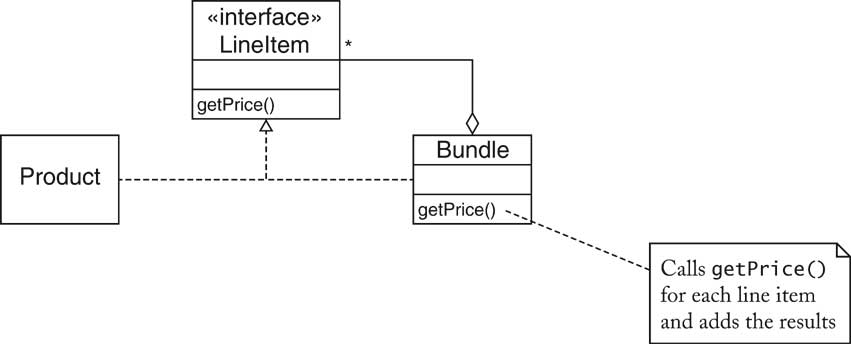
| Bundles [58/72] |
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/Bundle.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| Bundles [59/72] |
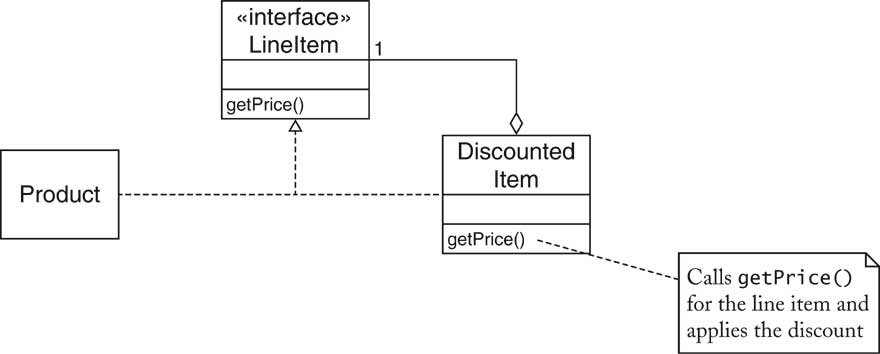
| Discounted Items [60/72] |
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/DiscountedItem.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| Discounted Items [61/72] |
| Model/View Separation [62/72] |
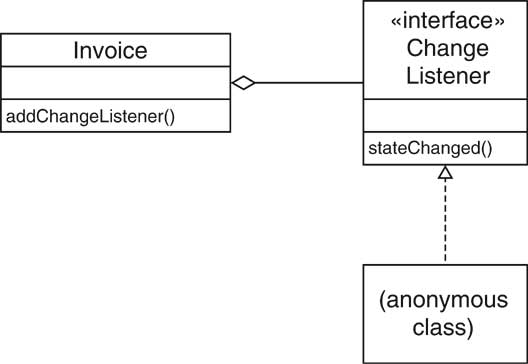
| Change Listeners [63/72] |
| Change Listeners [64/72] |
final Invoice invoice = new Invoice();
final JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea(20, 40);
ChangeListener listener = new
ChangeListener()
{
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent event)
{
textArea.setText(...);
}
};
| Observing the Invoice [65/72] |
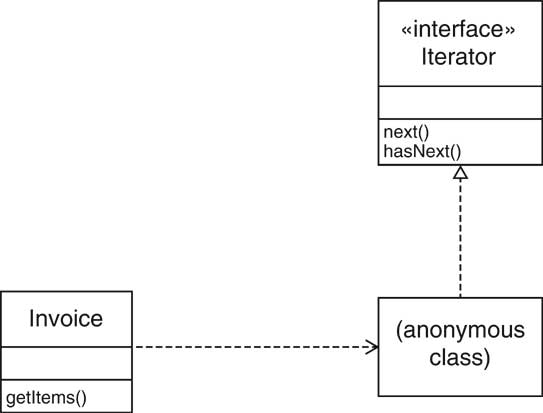
| Iterating Through Invoice Items [66/72] |
| Iterators [67/72] |
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/Invoice.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| Iterators [68/72] |
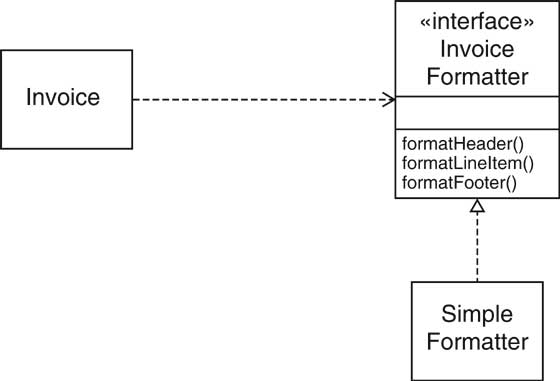
| Formatting Invoices [69/72] |
| Formatting Invoices [70/72] |
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/InvoiceFormatter.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/SimpleFormatter.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
file:horstmann/ch05_invoice/InvoiceTester.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| Formatting Invoices [71/72] |
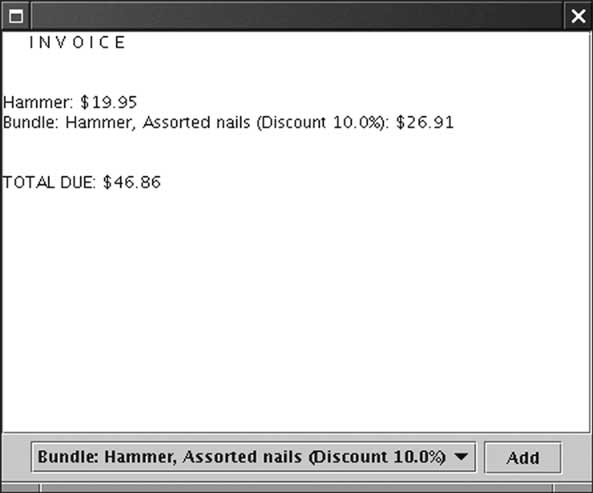
| Formatting Invoices [72/72] |
Revised: 2007/09/11 16:27